

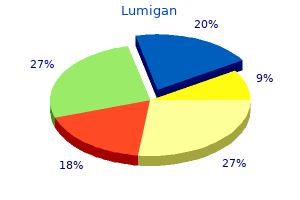
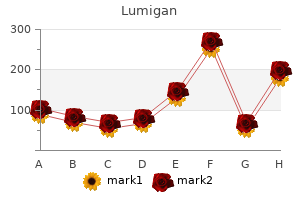
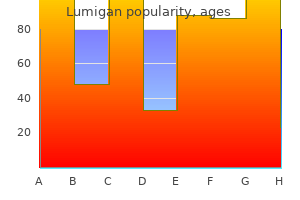
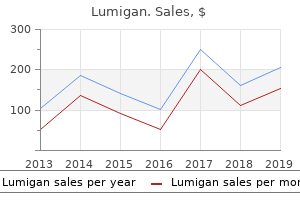
"Discount 3ml lumigan fast delivery, medications gout".
By: V. Avogadro, M.S., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Stony Brook University School of Medicine
That animals never suffer spondylolisthesis is proof enough to declare that this condition is a curse of erect posture symptoms before period cheap lumigan 3ml with mastercard, which only man prides to possess! Definition It is defined as slow anterior displacement of a vertebra at the lower lumbar spine medications on backorder discount lumigan online, generally accepted as the lowermost vertebra L5 slipping forward on the first sacral segment S1 (Fig top medicine generic 3 ml lumigan. Essential lesion is the interruption in the concavity of the pars interarticularis medicine in french order lumigan 3 ml without prescription. Spondylolysis: In this, the defect in the pars exists but without the forward slipping. Interesting facts about spondylolysis ?About 50 percent of the patients who present with isthmic spondylolysis do not progress to spondylolisthesis. H/o trauma present in 50 percent ?Common history of injury in adults and children Deformity ?lumbar lordosis ?Palpable step at L5?1 ?Torso is short ?Abdomen protruded forwards ?Transverse furrow at L5 ?Sacrum is vertical ?Buttocks flat and Hamstring tightness ?L5 spinous process prominently felt. Traumatic: this is due to fracture in other areas of the bony hook rather than the pars. Clinical Features the clinical features of different varieties of spondylolisthesis are shown in Table 31. However, increased lumbar lordosis and transverse furrow over the lower back are unmistakable features of spondylolisthesis (Figs 31. However, oblique view of the lumbar spine demonstrates the defect in the pars very accurately as a "Scottie dog" sign. The edges of the defect are smooth and rounded and suggest a pseudoarthrosis rather than acute fracture. Methods of Surgery Posterolateral fusion: this is the best method of fusing the slipped vertebra because it preserves the supporting soft tissues and has a high rate of fusion. Posterior fusion: In this method, postoperative and additional slip is frequent until the fusion is solid. This also has a high rate of pseudoarthrosis and has to be done with intertransverse fusion. Laminectomy: this mainly helps to relieve the neurological deficits and has to be followed by posterolateral fusion. Anterior interbody fusion: this is indicated for subtotal spondylolisthesis and is a risky and difficult procedure with doubtful efficacy. Methods of Fusion and Stabilization: Fusion is achieved in spondylolisthesis by putting autologous cancellous bone graft and Hartshill rectangle frame or Steffee plate and screws help obtain stabilization (Fig. Defective Growth or Poor Postural Habits Children: Stooping posture while reading. In severe deformity and in adults, surgical decompression and stabilization is advised. Types Knuckle Prominence of single spinous process indicating collapse of single vertebra. Methods of Examination Inspection: Look from the side and note if the thoracic curvature is regular, now determine if the kyphosis is mobile or fixed. Acute kyphosis is called gibbus and is due to single or two level vertebral involvements. Normal coxa vara is due to differential growth pattern of capital femoral and greater trochanteric epiphysis. Clinical Features Small stature, limp, waddling gait, upward shift of greater trochanter, decreased rotation and abduction of hip, pain, stiffness and flexion contractures are some of the important clinical features of coxa vara. The prognosis for a child with this disease has improved considerably than in the past. It is the most common form of osteochondroses, Classification Congenital ?Congenital coxa vara. Part of generalized skeletal dysplasias: this is seen in mucopolysaccharidosis, multiple epiphyseal dysplasias, achondroplasia, cleidocranial dysostosis, etc. Legg, Arthur Thornton, Massachusetts (1910) and Jacques Calve (1910) of France also described it and called it as coxa plana. Regional Conditions of the Lower Limb Pathogenesis of Legg-Calv?erthes disease Idiopathic capital femoral epiphyseal ischemia (initial infarction) 411 Sex: Eighty percent affected are males (4:1). Etiology the etiology remains unknown, but it is currently accepted that the disorder is caused by an interruption of the blood supply to the capital femoral epiphysis, causing avascular necrosis.
The two most prominent impingement diagnoses are known as Cam impingement and Pincer impingement medicine go down generic lumigan 3ml with visa. In both cases bony abnormalities lead to potentially further structural damage to the hip joint in treatment online lumigan 3 ml cheap. If the impingement problem is symptomatic with hip joint and groin pain symptoms 9 days post ovulation buy generic lumigan 3ml on-line, damage to the acetabular cartilage as well as to the labrum of the hip joint is often found medications derived from plants discount generic lumigan canada. These osseous hip problems need in most cases to be treated surgically if symptomatic, followed by a closely monitored rehabilitation program to re-establish muscle strength and coordination related to the pelvis. In some more rare types of hip dysplasia surgery can be indicated to prevent the development of osteoarthosis in the hip joint. It is not clear, whether any prevention is indicated in cases of pain-free impingement, but theoretically there is a risk, that these patients develop groin injury and intra-articular damage of the hip joint. How these athletes should be advised regarding further sports activities is not clear and is currently a subject for discussion and ongoing scientific studies. Strength training the strength of the abductor and the adductor muscles have been debated as possible risk factors earlier in this chapter. One study suggests that the ratio between adductors and abductors are important and that pre-season strength training of the adductor muscles in ice hockey players with adductor/abductor strength ratio 80% could decrease the number of adductor related groin injuries (Tyler et al. The study however had some methodological concerns and since other studies have been conflicting regarding the strength of the adductor and abductor muscles, 112 Chapter 7 the study does not provide conclusive evidence for this method of prevention. If, however, we also consider the protective effect of pre-season sportspecific training in ice hockey, this also has implications for supporting eccentric adductor strength activity to reduce the risk of groin injury. The combination of strengthening of the adductors and the abductors with abdominal and low back muscle recruitment is probably the area where some of the most likely possibilities are available. A randomized treatment study including specific training of the adductor muscles (static, concentric, and eccentric), as well as exercises for the muscles related to the pelvis including the core stability principles, showed a highly significant effect in the treatment of adductor-related groin injuries (H?ch et al. In another randomized controlled trial including 1022 male soccer players, the possible preventive value of such an exercise program has been examined. The trial found that the risk of sustaining a groin injury was decreased 31%, but the difference was not statistically significant. Despite the inconclusiveness of this study, the 31% reduction in the risk of getting a groin injury would be a considerable advantage, which probably would make it worth while for the soccer players to do the program. Additionally, pre-season sport-specific training may allow for further contraction and function-specific recruitment of these muscles which might allow for their more effective utilization and less onset of fatigue as the season progresses. Take-home message the best means to identify an athlete at risk for a groin injury may be for the athlete to undergo a preparticipation physiotherapy examination. Chapter 8 Preventing low back pain Adad Baranto1, Tor Inge Andersen2 and Leif Sw?3 1 2 Department of Orthopaedics, Sahlgrenska University, G?org, Sweden National Center of Spinal Disorders, National Center of Pain and Complex Disorders, Trondheim University Hospital, St Olav, Norway 3 Department of Orthopaedics, Sahlgrenska University, G?org, Sweden Epidemiology Increased training levels In the 1970s some studies showed positive effects of regular training among adolescents in physical fitness, technique, and coordination. This has led to a common opinion that high doses of training for long periods of time at a young age are required in order to become an elite athlete. Historically, this has resulted in a trend to start training, competition and specialization in one sport at a very young age. This means that many sports require training with high intensity and with high load, often from a very young age. In many sports, it has been found that athletic training with the aim of perfection requires monotonous and repetitive strenuous exercises, leading to an increased risk of musculoskeletal morbidity and/or disturbed growth. A result of this is that overuse injuries are an increasing problem in sports and have also been more noticed among young athletes. It has also been shown that the growing spine is highly vulnerable to trauma, especially during the adolescent growth spurt (Baranto et al. In many sports, such as gymnastics, wrestling, and weight lifting, the growing spine is exposed to high loads and in some situations to extreme loads. It is therefore not surprising that a "red flag" has been raised for the early selection of one sport and the early start of specialized training. Low back pain in young athletes Back pain symptoms in children and adolescents are different from those in adults and in many cases also have other causes than in adults (Sassmannshausen & Smith, 2002). The symptoms in children are less distinct and they rarely have neurological deficits as in adults. Physicians diagnosing back pain in young athletes must have a specific understanding of these differences in order to avoid incorrect diagnosis and harmful delays in proper treatment.
Clinical Features Symptoms Usually medicine 8 iron stylings order lumigan 3ml amex, it is symptom less medicine 44390 purchase 3 ml lumigan otc, but the patient may complain of pain medications after stroke 3 ml lumigan otc, swelling treatment hepatitis c generic lumigan 3ml without a prescription, etc. Signs A firm nontender swelling fixed to the bone around the joints is the most common clinical finding. Joint movements may be decreased because of the tumor causing a mechanical block rather than the extension of the tumor into the joint. The tumor is composed of cortical and medullary portions, which are continuous with the main bone. Treatment Usually, it requires no treatment, but complete surgical excision is indicated in the following situations: Joint interference: If the tumor is large and obstructing the joint movements, it needs excision of the tumor along with its periosteal cover to prevent recurrence of the tumor. Painful bursitis: A bursa usually develops because of the constant friction between the tumor and the surrounding soft tissues. If inflammation develops within this bursa, it gives rise to pain necessitating its excision. Malignant change (1-2%): Local irradiation may convert this benign tumor into malignant. Pressure on the neighboring vessels and nerves may give rise to neurovascular complications. It causes destruction of the cancellous bone and has a potential for undergoing malignant change, especially when it is situated in the long bones. Radiographs the tumor appears cystic (loculated or nonloculated), cortex is thin and expanded, it may be perforated; and at the center, fibrous septa may be seen interspersing the central cavity (Fig. The surgery done in cases of large tumors is excision and removal of the capsule to prevent recurrence. Prognosis the incidence of malignant change is 25 percent, especially in the pelvis. Here the cancellous bone is destroyed and multiple calcium deposits are usually found within the tumor. Radiographs Radiographic features of the tumor are areas of rarefaction at epiphysis, eccentric position of the tumor, thin cortex and mottled areas of calcification. Treatment this consists of curettage and bone grafting if the lesion is small, excision in bigger tumors. Unlike osteogenic sarcoma, there is no neoplastic osteoid formation and alkaline phosphatase is usually not raised. Classification Primary/secondary: Secondary tumors develop when benign cartilaginous tumors are irradiated. Peripheral/central/juxtacortical: Depending on the situation of the tumor within the bone. Location: It is common at the sites of proximal femur, humerus, ribs, scapula, innominate bones, rare in hands and feet except in calcaneus, occur in pelvis or upper femora. Clinical Features Symptoms: the duration of symptoms are usually less than 2 years in 75 percent of the cases and less than 5 years in the remaining 25 percent. The central tumor remains entirely asymptomatic until it has eroded and penetrated the cortex or caused a pathological fracture. A palpable firm mass attached to the bone is the common physical 622 General Orthopedics cation is observed in slow growing tumors. Peripheral tumors: these are very large tumors and the central part is heavily calcified. Forequarter amputation (Thikor-Linberg) for the shoulder girdle; hindquarter amputation for the pelvic girdle. High-grade lesions: Require radical marginal excision Role of systemic chemotherapy in chondrosarcoma is controversial. Palliative radiotherapy is indicated when the tumor cannot be resected because of its enormous size or if the tumor is present in inaccessible region. Cytological features: Suggesting high-grade malignancy are: ?Increased water and calcium (85%). Radiographs Central tumors Central lytic lesion with calcification gives a fluffy, cotton wool, popcorn or breadcrumb appearance (Fig.
Newer techniques: ?Limb salvage with tumor endoprosthesis: this is showing a better final clinical outcome in recent times treatment improvement protocol purchase lumigan now. Megavoltage radiotherapy Megavoltage irradiation is given preoperatively before amputation to decrease the viability of the cells that may be disseminated into bloodstream by surgical trauma treatment warts lumigan 3ml free shipping. The remaining 40 percent become disease free due to aggressive attack on the metastasis treatment 5 alpha reductase deficiency order lumigan 3 ml fast delivery. After metastasis has occurred treatment impetigo order lumigan online from canada, chemotherapy decreases the tumor size and enables easy surgical removal. By using the above drugs in short cyclical courses, toxic effects can be held to a minimum. Addition of an alkylating agent, like cyclophosphamide, has increased the interval between the administrations of individual drugs. In summary, after having established the diagnosis of osteogenic sarcoma with certainty, the patient is initially put on chemotherapy. Treatment of Pulmonary Metastasis Pulmonary microemboli are best managed by chemotherapy. Large lesions require removal by wide resection or lobectomy after giving chemotherapy. Another experimental approach to manage the lethal metastasis is the immunological approach. Prognosis Prognosis of osteogenic sarcoma has dramatically improved by the combined approach of ablation, megavoltage irradiation and chemotherapy. In untreated cases, survival time after pulmonary metastasis has developed (around 2. With the combined approach of chemotherapy, radiotherapy and pulmonary resection, the five-year survival rate has increased by 60 percent. Osteogenic sarcoma is curable and warrants intensive treatment with chemotherapy and surgical resection. Remember Characteristic facts of osteogenic sarcoma ?Highly malignant bone tumor. Radiographs Radiographic features of the tumor consist of radiolucent area situated at the metaphysis. It extends outwards eccentrically, periosteal new bone formation is seen, and pathological fractures may be present (Figs 44. It is an uncommon, non-neoplastic lesion commonly seen in the first two decades of life. It is situated in the metaphysis of the long bones and its proximity towards the epiphysis may affect the growth plate. The cyst will not disappear on its own and remains so unless obliterated by surgery. Age: Fifty percent lesions are seen in less than 10 years of age, forty percent between 10 and 20 years. Pathology Gross: It is a fusiform swelling, occupying the metaphyseal region of the bone. Types of Cyst There are two types of bone cysts: Active cyst is so called if the cyst is situated close to the epiphyseal plate. Clinical Features the tumor is asymptomatic until fracture occurs through the cyst wall, which causes pain and draws the attention of the patient towards the problem. Due to its proximity to the growth plate, the cysts may cause shortening, lengthening, coxa vara or coxa valga deformities. The tumor weakens the bone and the patient is susceptible to pathological fractures. Spontaneous obliteration of the cyst is seen in 15 percent of the cases and in 30 percent of the cases, cyst is displaced down the shaft due to continuous bone growth. Radiographs Radiographic examination of the tumor shows lytic lesion in the juxtaepiphyseal portion of the metaphysis, the lesion is expansive, the regional cortex is attenuated and pathological fractures may be seen (Figs 43. Subtotal resection and bone grafting here: One cm of the normal bone above and below the lesion is excised.
Discount 3ml lumigan free shipping. Suboxone withdrawal day 9-10.
