

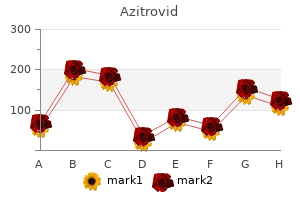
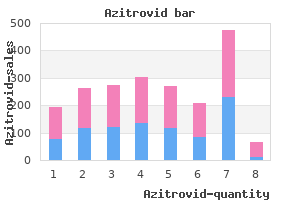
"Buy 100mg azitrovid, antimicrobial use density".
By: X. Ayitos, M.A., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, University of South Carolina School of Medicine Greenville
Family Serranidae Grouper Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides Hamilton antibiotics for acne long term effects cheap 250mg azitrovid mastercard, and E antibiotics for acne nhs discount azitrovid 500 mg on-line. Streptococcosis 847 848 Blenny zinnat antibiotic buy cheap azitrovid, Viviparous blenny (Zoarces viviparus Linnaeus) Atypical Aeromonas salmonicida Red ulcers with white margins virus - ruchki zippy purchase azitrovid once a day. Haemorrhage and ulcerative lesions Not susceptible to infection with 225 569 Streptococcus iniae 848 1. Pseudomonas anguilliseptica Common bream, Carp bream (Abramis brama Linnaeus) Aeromonas salmonicida ssp. No external changes except anus red and protruded, abdomen distended, fluid in abdominal cavity, congested spleen, petechial haemorrhages on liver, granulomatous lesions in spleen and kidney, multifocal tissue necrosis 4. Ulcers, haemorrhages, exophthalmia Large open skin lesions surrounded by areas of descalation. Tenacibaculum maritimum Aquatic Animal Species and Organism Relationship Sea bream (Sparus auratus Linnaeus). Primary pathogens in virulence studies 57 58 60 96 225 242 751 786 853 Silver bream, White bream (Blicca bjoerkna Linnaeus) Aeromonas salmonicida ssp. Ascites Haemorrhage in eyes, swollen, dark coloured abdomen, yellow liver, yellow fluid in intestine External haemorrhage, tail rot Mortality 1, 3. Ref 135 209 234 271 379 425 452 473 760 51 Host Pathogen Common carp, Koi carp (Cyprinus carpio carpio Linnaeus) 1. Yersinia ruckeri Caucasian carp, Crucian carp (Carassius carassius Linnaeus) Escherichia vulneris Chapter 1 Iberian toothcarp, Spanish toothcarp (Aphanius iberus Valenciennes) Vibrio parahaemolyticus Mortality 10 Silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix Valenciennes) 1. Large red ulcerative lesions on the abdomen, base of the pectoral fin and on the head. Rafinesque) Flavobacterium columnare Black bullhead (Ameiurus melas valid name), (Ictalurus melas Rafinesque scientific name) 1. Flavobacterium columnare Blue catfish (Ictalurus furcatus Valenciennes) Edwardsiella ictaluri 334 Brown bullhead (Ictalurus nebulosus) 1. Infection in the brain, systemic dissemination and localization of the organism in the visceral organs and musculature and cutaneous ulcers 2. Bacteria isolated from lesions on skin and superficial muscle, necrosis in organs 6. Haemorrhagic rings around the eyes and frontal foramens Mortality, multifocal irregular, white lesions on internal organs. Edwardsiellosis, enteric septicaemia, opportunistic infection Yersiniosis 73 203 307 334 547 783 1. Yersinia ruckeri Freshwater catfish, Sutchi catfish (Pangasius hypophthalmus Sauvage) Edwardsiella ictaluri Bacillary necrosis of Pangasius 194 Walking catfish (Clarias batrachus Linnaeus) (Clarias gariepinus) 1. Non-pathogenic 29 426 334 837 599 767 186 232 599 712 767 White catfish (Ameiurus catus Linnaeus) Edwardsiella ictaluri Chub, European chub (Leuciscus cephalus Linnaeus) Atypical Aeromonas salmonicida Aquatic Animal Species and Organism Relationship Coalfish 4. Photobacterium iliopiscarium Photobacterium iliopiscarium Cod, Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua Linnaeus) 1. Ref 59 458 742 83 84 212 Host Pathogen Coral Oculina patagonica Vibrio shilonii (said to be a later subjective synonym of V. Organism also found in lungs Cutaneous lesions Septicaemia Exudative polyarthritis 408 408 441 453 Australian freshwater crayfish Vibrio mimicus Yabby (Cherax albidus) Red claw (Cherax quadricarinatus) Crevalle, Trevally, Jack crevalle (Caranx hippos Linnaeus) Vibrio harveyi Edwardsiella tarda Crocodile Crocodilus acutus Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Caiman crocodile (Caiman crocodilus) Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Crocodylus niloticus Mycoplasma crocodyli Dab (Limanda limanda Linnaeus) Round, red ulcers with white margin of necrotic tissue 832 323 352 1, 2. Infection Skin ulcers Atypical Aeromonas salmonicida Dace, Common dace (Leuciscus leuciscus Linnaeus) 1. Atypical Aeromonas salmonicida Damselfish (Family Pomacentridae) Skin ulcers Fatal infection due to production of a cytolysin Infection, mortality 504 572 Blacksmith (Chromis punctipinnis Cooper) Photobacterium damselae ssp. Focal lesions progress to large de-pigmented necrotic patches then detach at dermo-epidermal junction to form large ulcers that expose underlying muscle 7. Ulcerative skin disease, morbidity 584 Eel American eel (Anguilla rostrata Lesueur) 1. Aeromonas salmonicida Aquatic Animal Species and Organism Relationship European eel (Anguilla anguilla Linnaeus) 1.
Syndromes

Bias due to selection of the outcome measure occurs when an effect estimate for a particular outcome is selected from among multiple measurements bacteria 0157 order azitrovid 100mg fast delivery, for example when a measurement is made at a number of time points or using multiple scales antibiotics for sinus infection australia purchase discount azitrovid line. Bias due to selection of the analysis occurs when the reported results are selected from intervention effects estimated in multiple ways antimicrobial mouth rinse over the counter cheap 100mg azitrovid otc, such as analyses of both change scores and post-intervention scores adjusted for baseline antibiotics for uti without sulfa purchase 100mg azitrovid with mastercard, or multiple analyses with adjustment for different sets of potential confounders. Review authors are also encouraged to list important co-interventions in their protocol. Relevant co-interventions are the interventions or exposures that individuals might receive after or with initiation of the intervention of interest, which are related to the intervention received and which are prognostic for the outcome of interest. Therefore, co-interventions are a type of confounder, which we consider separately to highlight its importance. Important confounders and co-interventions are likely to be identified both through the knowledge of subject-matter experts who are members of the review team, and through initial (scoping) reviews of the literature. Discussions with health professionals who make intervention decisions for the target patient or population groups may also be helpful. Assessment of risk of bias may, for some domains, rely heavily on expert opinion rather than empirical data: this means that consensus may not be reached among experts with different opinions. Often the description of these interventions will require subject-matter knowledge, because information provided by the investigators of the observational study is insufficient to define the target trial. Meaningful assessment of risk of bias is problematic in the absence of well-defined interventions. An analogue of the effect of adhering to the intervention as described in the trial protocol is (starting and) 627 25 Risk of bias in a non-randomized study adhering to experimental intervention versus (starting and) adhering to comparator intervention unless medical reasons. Review authors should seek specialist advice when assessing intervention effects estimated using methods that adjust for time-varying confounding. When the effect of interest is that of assignment to the intervention (or starting intervention at baseline), risk-of-bias assessments need not be concerned with postbaseline deviations from intended interventions that reflect the natural course of events. The only post-baseline deviation that may lead to bias are the potentially biased actions of researchers arising from the experimental context. Observational studies estimating the effect of assignment to intervention from routine data should therefore have no concerns about post-baseline deviations from intended interventions. The signalling questions aim to elicit information relevant to the risk-of-bias judgement for the domain, and work in the same way as for RoB 2 (see Chapter 8, Section 8. When exclusion of some eligible participants, or the initial follow-up time of some participants, or some outcome events, is related to both intervention and outcome, there will be an association between interventions and outcome even if the effect of interest is truly null. A specific example is bias due to the inclusion of prevalent users, rather than new users, of an intervention. Bias introduced by either differential or nondifferential misclassification of intervention status. Non-differential misclassification is unrelated to the outcome and will usually bias the estimated effect of intervention towards the null. Differential misclassification occurs when misclassification of intervention status is related to the outcome or the risk of the outcome. Bias that arises when there are systematic differences between experimental intervention and comparator groups in the care provided, which represent a deviation from the intended intervention(s). Assessment of bias in this domain will depend on the effect of interest (either the effect of assignment to intervention or the effect of adhering to intervention). Bias that arises when later follow-up is missing for individuals initially included and followed. Such bias can arise when outcome assessors are aware of intervention status, if different methods are used to assess outcomes in different intervention groups, or if measurement errors are related to intervention status or effects. Selective reporting of results from among multiple measurements of the outcome, analyses or subgroups in a way that depends on the findings. The study is sound for a non-randomized study with regard to this domain but cannot be considered comparable to a well-performed randomized trial. The study is too problematic in this domain to provide any useful evidence on the effects of intervention. These differ from the risk-of-bias judgements for the RoB 2 tool (Chapter 8, Section 8. Because of confounding, we anticipate that only rarely will design or analysis features of a non-randomized study lead to a classification of low risk of bias when studying the intended effects of interventions (on the other hand, confounding may be a less serious concern when studying unintended effects of intervention (Institute of Medicine 2012)). Brief, direct quotations from the text of the study report should be used whenever possible.
Having clearly documented rationale ensures that every measure is justified and has an "evidence trail" antimicrobial step 1 order azitrovid with a visa. Information on anatomic extent of disease (stage) at presentation significantly enhances incidence and mortality data in understanding the cancer burden infection resistant legguards buy azitrovid 250mg cheap. Once a cancer registrar had identifies the presence of metastatic disease (M1) this is recorded and additional information is unnecessary to establish that stage of disease bacteria blood purchase azitrovid 500mg otc. In turn if there is no nodal disease the extent/size of the primary carcinoma is recorded antibiotics for neck acne buy azitrovid from india. The field tests however identified three key issues: the underidentification of distant metastases, inaccurate the collection of lymph node data and improved training needs. In particular there was uncertainty in the identification of when lymph node involvement was considered to be distant metastatic or regional. In view of this, refinements to the schemas have been made to simplify the collection of nodal data. Ogunbiyi2 1 Ibadan Cancer Registry, University of Ibadan/University College Hospital, Ibadan, Nigeria; 2Ibadan Cancer Registry, Department of Pathology, University of Ibadan/University College Hospital, Ibadan, Nigeria Background and context: Routine collection of quality oncology data remains underprioritized in resource limited settings. Strategy/Tactics: Conventional routine data quality assessments guide iterative identification of data quality gaps for improvement, but tend to consume additional human resources to implement and prioritize data quality over existing provider concerns. Program/Policy process: A need assessment began with mapping of patient care process, capturing process steps, including subprocesses, actors, and an inventory of related data capture systems. Providers indicated the overbooking of patient appointments and use of different formats to manage patient data as key challenges for them. Cases are abstracted from the main teaching hospital, designated private hospitals and clinics representing active practices, National Population Commission and private laboratories. We observed a decline in numbers of cases registered compared with what was projected and moved to effect corrections to this decline. In addition to reviewing our usual sources, we enlisted more sources of case recruitment. Aim: this study was done to assess the impact of additional sources of data collection on the number of cases recorded in the registry. Strategy/Tactics: the registry had improved contact with the local Ministry of Health and local governments administration, identified new facilities that treat cancer patients and new histopathologic laboratories that diagnose cancers. Program/Policy process: the registry enlisted cases from thirty (30) sources during 2009-2012 time period. In the 2013-2016 period, the registry improved the data collection sources to sixty (60) due to good advocacy, improved collaborative effort with our partners and very active case finding. Outcomes: A total of 3116 cases were recorded in the registry during the period 2009-2012. This increased to 3744 in the period 2013-2016 giving a 20% increase in the number of abstracted cases in the latter period. The ranking order of cancer in the population we serve changed from breast, cervix and prostate cancers in 2009-2012 to breast, prostate and cervix in the second time period. What was learned: Changes in health providing facilities affect the recruitment of new cancer cases into the database of cancer registries. Furthermore, cancer registries must always improve the database of sources where cases are recruited, as this is dynamic. Good advocacy, very active case finding and improved relation with the community have increased the number of cases of cancer recorded in our registry. Wu1 University of Tianjin, Tianjin, China; 2Tianjin Medicial University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Tianjin, China; 3China Anti-Cancer Association, Tianjin, China Background and context: Cancer is not only a medical problem, but also a socioeconomical issue as the high prevalence with poor prognosis brings heavy financial burden to the society. From 2005 to 2013, the incidence and mortality rates have sharply increased in China. The most common types of cancer in males in China are lung cancer, gastric cancer, and liver cancer while breast cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer are the major types of cancer among Chinese females. The prognosis for most types of cancer is poor and the treatment costs have been high and hence cancer has caused significant financial burden on patients and negatively impacted their lives. Since the 1970s, Chinese government has been paying attention to cancer burden and applying the nationwide cancer management strategy. Population-based cancer screening, public health education of cancer prevention and treatment on general population, and catastrophic disease medical insurance policy providing additional funding for cancer treatments have been widely implemented in the country.
This approach can be feasible when a review question involves multiple publication types antibiotics muscle pain buy azitrovid online. This method relies on reports of process evaluations also describing the surrounding randomized trial in enough detail to be identified by the search filter infection large intestine cheap azitrovid 100 mg without a prescription. Approaches using strings of terms associated with the study type or purpose are considered experimental antibiotic resistance fitness cost purchase 500mg azitrovid fast delivery. It is likely that such filters may be derived from the study type (process evaluation) antibiotic generic names discount 250mg azitrovid fast delivery, the data type (process data) or the application (implementation) (Robbins et al 2011). However, within systematic reviews and evidence syntheses it is considered essential, even when studies are not to be excluded on the basis of quality (Carroll et al 2013). One review found almost 100 appraisal tools for assessing primary qualitative studies (Munthe-Kaas et al 2019). Limitations included a focus on reporting rather than conduct and the presence of items that are separate from, or tangential to , consideration of study quality. In the absence of a definitive risk to rigour tool, we recommend that review authors select from published, commonly used and validated tools that focus on the assessment of the methodological strengths and limitations of qualitative studies (see Box 21. Issues such as inter-rater reliability are afforded less importance given that identification of complementary or conflicting perspectives on risk to rigour is considered more useful than achievement of consensus per se (Noyes et al 2019). Tools not meeting the criterion of focusing on assessment of methodological strengths and limitations include those that integrate assessment of the quality of reporting (such as scoring of the title and abstract, etc) into an overall assessment of methodological strengths and limitations. As with other risk of bias assessment tools, we strongly recommend against the application of scores to domains or calculation of total quality scores. Being reflexive entails making conflicts of interest transparent, discussing the impact of the reviewers and their decisions on the review process and findings and making transparent any issues discussed and subsequent decisions. Evidence suggests that qualitative sensitivity analysis is equally advisable for mixed methods studies from which the qualitative component is extracted (Verhage and Boels 2017). Decisions on whether to include all studies or to select a sample of studies depend 533 21 Qualitative evidence on a range of general and review specific criteria that Noyes and colleagues (Noyes et al 2019) outline in detail. The number of qualitative studies selected needs to be consistent with a manageable synthesis, and the contexts of the included studies should enable integration with the trials in the effectiveness analysis (see Figure 21. The guiding principle is transparency in the reporting of all decisions and their rationale. Flexible options concerning choice of method may need to be articulated in the protocol. Some methods are designed primarily to develop findings at a descriptive level and thus directly feed into lines of action for policy and practice. Noyes and colleagues (Noyes et al 2019) and Flemming and colleagues (Flemming et al 2019) elaborate on key issues for consideration when selecting a method that is particularly suited to a Cochrane Review and decision making context (see Table 21. Three qualitative evidence synthesis methods (thematic synthesis, framework synthesis and meta-ethnography) are recommended to produce syntheses that can subsequently be integrated with an intervention review or analysis. Findings may be presented as a narrative, or summarized and displayed as tables, infographics or logic models and potentially located in any part of the paper (Noyes et al 2019). Methods for qualitative data extraction vary according to the synthesis method selected. Data extraction is not sequential and linear; often, it involves moving backwards and forwards between review stages. Review teams will need regular meetings to discuss and further interrogate the evidence and thereby achieve a shared understanding. It may be helpful to draw on a key stakeholder group to help in interpreting the evidence and in formulating key findings. Additional approaches (such as subgroup analysis) can be used to explore evidence from specific contexts further. Requires some caution in its use Framework synthesis (Oliver et al 2008, Dixon-Woods 2011) Best-fit framework synthesis (Carroll et al 2011) Pros: Works well within reviews of complex interventions by accommodating complexity within the framework, including representation of theory. The framework allows a clear mechanism for integration of qualitative and quantitative evidence in an aggregative way see Noyes et al (2018a). Works well where there is broad agreement about the nature of interventions and their desired impacts. A framework may be revealed as inappropriate only once extraction/ synthesis is underway. Requires more caution in its use Meta-ethnography (Noblit and Hare 1988) Pros: Primarily interpretive synthesis method leading to creation of descriptive as well as new high order constructs. Descriptive and theoretical findings can help inform decision making such as guidelines.
Discount azitrovid online american express. Key Elements of Successful Antimicrobial Stewardship.
