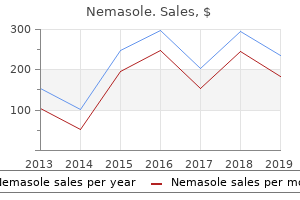
"Purchase nemasole 100 mg without prescription, hiv infection rate from needle stick".
By: V. Eusebio, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of Kentucky College of Medicine
Second antivirus walmart buy discount nemasole 100mg online, superinfections and spontaneous bacteremia from endogenous sites of enterococcal colonization are described in patients receiving quinolone or moxalactam antibiotics antiviral ribavirin generic 100mg nemasole fast delivery. Last hiv infection rates zimbabwe order nemasole with american express, conjugational transfer of plasmids and transposons between enterococci in the face of intense antibiotic pressure within the hospital mileu have created multidrug-resistant strains hiv infection lawsuit nemasole 100 mg overnight delivery, including those with vancomycin and teicoplanin resistance. Acquired resistance to glycopeptide in enterococci is due to the production of peptidoglycan precursors ending in the dipeptide D-alanine- D-lactate ( D-alaD-lac) instead of the dipeptide D-ala- D-ala, which is found in susceptible bacteria. This substitution prevents the formation of complexes between glycopeptides and peptidoglycan precursors at the cell surface that are responsible for inhibition of cell wall synthesis. The majority of enterococci harboring Van B-type gene clusters are inducibly resistant to vancomycin but remain susceptible to teicoplanin because induction occurs only in the presence of vancomycin. Serious enterococcal infections such as endocarditis or bacteremia require a synergistic combination of antimicrobials such as ampicillin or vancomycin, together with an aminoglycoside. Teicoplanin may be substituted for vancomycin if Van B-type resistance is present. Unfortunately, some strains of enterococci are resistant to all known antibiotics. These organisms may be isolated from the throats of both humans and dogs, produce streptolysin O, and resemble group A in colony morphology and spectrum of clinical disease. Before rapid identification tests were developed, many infections caused by groups C and G were mistakenly attributed to group A, such as pharyngitis, cellulitis, skin and wound infections, endocarditis, meningitis, osteomyelitis, and arthritis. These strains also cause recurrent cellulitis at the saphenous vein donor site in patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass surgery. Both organisms are susceptible to penicillin, erythromycin, vancomycin, and clindamycin. They normally colonize the oropharynx, upper gastrointestinal tract, and appendix. Infections are most commonly related to contiguous abscess formation such as a tooth abscess or periapendiceal abscess. Primary bacteremia with or without endocarditis and metastatic abscesses of the brain, lung, bone, joints, liver, and spleen are characteristic of S. These organisms are recognized as gray-white colonies, slightly larger than group A streptococci, but with a narrower zone of hemolysis. Definitive identification is made with group-specific antiserum or commercial kits that use agglutination end points. The polysaccharide capsule is the prime virulence factor in group B streptococci and is instrumental in the evasion of phagocytosis. Group B streptococci are the most common cause of neonatal pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis in the United States and western Europe, with an incidence of 1. Preterm infants born to mothers with premature rupture of membranes who are colonized with group B streptococci are at highest risk for early-onset pneumonia and sepsis. The mean time of onset is 20 hours, and symptoms are respiratory distress, apnea, fever, and hypothermia. Ascent of the streptococcus from the vagina to the amniotic cavity causes amnionitis. Infants may aspirate streptococci either from the birth canal during parturition or from amniotic fluid in utero. Radiographic evidence of pneumonia and or hyaline membrane disease is present in 40% of neonates with infection, and meningitis occurs in 30 to 40% of cases. Late-onset neonatal sepsis occurs 7 to 90 days postpartum, with symptoms of fever, poor feeding, lethargy, and irritability. Adults with group B infections include postpartum women and patients with peripheral vascular disease, diabetes, or malignancy. Soft tissue infection, septic arthritis, and osteomyelitis are the most common findings. Although penicillin is the treatment of choice, in practice many neonates are empirically treated with ampicillin (300 to 400 mg/kg/day) plus gentamicin. Once the diagnosis is established, penicillin at 200 to 500,000 U/kg/day should be given. Adults should receive 10 to 12 million U of penicillin per day for bacteremia, soft tissue infection, or osteomyelitis, but the dose should be increased to 18 to 24 million U/day for meningitis. Vancomycin and a 1st-generation cephalosporin are alternatives for penicillin-allergic patients. Intrapartum administration of ampicillin to women colonized with group B streptococcus who also had premature labor or prolonged rupture of membranes prevents group B neonatal sepsis.
All tissues constantly utilize glucose either for energy purposes or for conversion into other products (glycogen hiv infection rate definition generic nemasole 100 mg on line, pentoses antiviral brandon cronenberg order nemasole 100mg without a prescription, lipids hiv infection lawsuit discount nemasole 100mg overnight delivery, amino acids) hiv virus infection process video nemasole 100 mg lowest price. Therefore, an outflow of glucose from the circulation, which is governed by the rate of utilization of glucose by a tissue, occurs at all times. The level of blood glucose itself partially governs the rate of utilization and therefore, in a sense, is autoregulatory. At high levels, the rate of glucose uptake by tissues such as muscle and liver increases because of mass action. The action of insulin is opposed by the diabetogenic factors, growth hormone, glucagon, cortisol, and epinephrine. The liver occupies a central position in the regulatory mechanism of blood glucose concentration because it supplies as well as removes glucose from the system. The major direction of liver glucose metabolism is directed toward supplying rather than using glucose. This glycogen is the source of the glucose supplied by the liver to the system during the better part of a day. Muscle, on the other hand, does not contain G-6-Pase, so it cannot provide free glucose and is therefore primarily a glucose-utilizing tissue. In the liver, however, glucose moves freely across the plasma membrane, so this process is not rate limiting at this point. This level is termed the "steady state" or the "glucostatic level" at which the mechanisms of normal supply and removal of glucose are operating at equal rates. This means that the liver supplies glucose throughout most of a day except for the few periods during the day when blood glucose is greater than the steady-state level of 8. The net result is an increase in glucose uptake by the liver with increased glucose oxidation, glycogenesis, and hypoglycemia. This directional control is due to the action of insulin on key enzymes of glucose metabolism. Directional control for glucose production or utilization is governed by coupled sets of opposing and irreversible enzyme reactions at three control points of glucose metabolism. The kinases direct metabolism toward glycolysis utilization because they are phosphorylating enzymes and the opposing enzymes reverse the direction so they are gluconeogenic. The opposing G-6-Pase reaction increases during fasting or starvation, which favors liver glucose production. Increases in activity of these gluconeogenic enzymes in insulin deficiency direct metabolic pathways toward excessive production of glucose by the diabetic liver. The amelioration of diabetes in an experimental animal by hypophysectomy (Houssay animal) is well established. The glucocorticoids increase gluconeogenesis and intracellular G-6-P and, by their insulin opposing effect, increase free glucose. An increase also results from the glycogenolytic action of epinephrine and glucagon, and the equilibrium is shifted to favor of glucose production. Therefore, it is the balance of hormones that directly (insulin) or indirectly (epinephrine, growth hormone, glucagon, cortisol) affects glucose metabolism, which sets the "steady-state blood glucose" at which the liver neither uses glucose or produces glucose. In 30 to 60 min, the peak level of blood glucose is reached, after which it begins to fall. At the same time, hepatic glucose output decreases and the blood glucose falls rapidly. When the blood glucose reaches its baseline level, it continues to fall below the original level for a short time and then returns to its baseline level. Clinically, this postinsulin hypoglycemia can be marked if there is a defect in the secretion of glucagon. Glucose Tolerance the regulatory events that occur in response to changes in blood glucose concentration are best summarized by a description of the events following ingestion of a test dose of glucose. When administered orally to a normal animal, a typical change in blood glucose concentration with time is observed as shown in Figure 3-12. During the absorptive phase, phase I, the rate of entry of glucose into the circulation exceeds that of removal and the blood glucose rises. As the blood glucose rises, hepatic glucose output is inhibited and the release of insulin from the pancreas is stimulated by the rising blood glucose. This principle is also used in the glucose-specific paper strips for urine glucose.
The complex repetitive discharge differs from myotonia in that it starts and stops abruptly and does not wax and wane in frequency and amplitude antiviral nucleoside analogues buy 100mg nemasole fast delivery. A fasciculation represents a spontaneous discharge of a motor unit hiv infection in south africa discount 100mg nemasole fast delivery, which is a group of muscle fibers of the same histochemical type under control of a single anterior horn cell describe the hiv infection cycle purchase 100 mg nemasole with amex, and thus innervated by the same axon hiv infection rates in the world nemasole 100 mg generic. Electrically a fasciculation is a large-amplitude potential that consists of the simultaneous involuntary depolarization of a group of muscle fibers. Although they do not necessarily imply neuromuscular disease and occur in many normal patients, fasciculations can occur in diseases of the motor neuron or nerve. When the patient voluntarily contracts the muscle, individual motor unit action potentials are assessed. Individual motor units are analyzed for their amplitude, duration, and number of phases. In addition, the firing rate and recruitment pattern of the voluntary motor units are noted. Two abnormal motor unit patterns that can be observed suggest that the disease is either "neuropathic" or "myopathic. In addition, for a given degree of voluntary effort, few motor units are recruited and the ones that are fire too rapidly (>15-20 Hz). This indicates a loss of motor units with a compensatory increased firing rate in the remaining units, a pattern known as decreased recruitment. Myopathic motor unit potentials are small, brief polyphasic potentials (<4 milliseconds). In a myopathy, multiple small motor units are recruited with only minimal voluntary effort. This myopathic pattern occurs because the number of motor units is normal but there are fewer functioning muscle fibers within each unit, and therefore more units are required to generate a degree of force. A muscle specimen can be obtained through either an open or a closed (needle or punch) biopsy procedure. Whether an open or punch biopsy procedure is performed, the tissue must be processed in a laboratory that is skilled in the evaluation of muscle and experienced in the specialized techniques needed for the assessment of the tissue. Biopsy specimens are analyzed by light and electron microscopy, biochemical studies, and molecular genetic studies. In most instances, light microscopic observations are sufficient to make a pathologic diagnosis. Muscle tissue examination under light microscopy is primarily performed by using frozen specimens. The tissue is examined for muscle fiber size, shape, fiber type distribution, presence of fiber degeneration (necrosis), and regeneration. Structural changes such as central nuclei, disorganization of myofibrils and sarcoplasm. Connective tissue and blood vessels are examined for inflammation, and it is determined whether there are increased collagen and fat. Type 1 fibers (slow-twitch, fatigue-resistant, oxidative metabolism) stain lightly at alkaline and darkly at acidic pHs. Type 2 fibers (fast-twitch, fatigue-prone, glycolytic metabolism) stain darkly at alkaline and lightly at acidic pHs. Qualitative biochemical enzyme stains can 2206 be performed for phosphorylase and phosfructokinase. Immunologic techniques can stain for muscle proteins that are deficient in some muscular dystrophies. The muscle biopsy result can be useful in order to establish whether there is evidence of either a neuropathic or a myopathic disorder. A neuropathy can produce denervation atrophy with small angular fibers, groups of atrophic fibers, and, as a result of reinnervation, groups of fibers of the same histochemical type and target fibers. Typical myopathic abnormalities include central nuclei, both small and large hypertrophic round fibers, split fibers, and degenerating and regenerating fibers. Inflammatory myopathies produce mononuclear inflammatory cells in the endomysial and perimysial connective tissue between fibers and occasionally around blood vessels.
However hiv infection rates by year order nemasole online now, worsening hirsutism is easily prevented with antiandrogen therapy hiv infection rates in australia buy discount nemasole 100 mg line, and most women experience a satisfactory improvement with the judicious use of mechanical and medical therapies antiviral drugs name buy line nemasole. Dunaif A hiv infection primary symptoms nemasole 100mg with visa, Givens J, Merriam G, Haseltine F (eds): Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (Current Issues in Endocrinology and Metabolism). A somewhat different approach (from mine) to the evaluation and treatment of hirsutism. A detailed review of the pathophysiology, evaluation, and treatment of hyperandrogenism. Lobo Menopause is defined as the last menstrual period and has a median age of 51. Age at menopause has not changed over the past few centuries while there has been a gradual increase in life expectancy. Thus, whereas in previous centuries women were not expected to live beyond menopause, women now spend one third to one half of their lives after menopause. Because menstrual cycles rarely cease abruptly, there is a period of time, termed the perimenopause or menopausal transition, during which there is a wide fluctuation in the hormonal profiles. In general, the perimenopause begins a few years before the last menstrual period (menopause) when cycles become irregular and there are often, but not always, symptoms suggesting a declining estrogen status. Although estrogen levels can be higher than normal early in the perimenopause, an abrupt decline in estrogen occurs 6 months before menopause. The perimenopause also extends for a few years beyond the menopause, a time during which transient and episodic bursts of 1361 ovarian activity may occur that may result in some vaginal bleeding. Reproductive aging occurs rapidly after the third decade, and fecundity is extremely low before menopause. Thus, reproductive aging precedes menopause by 5 to 10 years, at a "young" chronologic age. These values may be elevated only intermittently before they continue to rise at the time of menopause. The most significant findings are the marked reductions in estradiol (E2) and estrone (E1). Serum E1, on the other hand, is produced primarily by peripheral aromatization from androgens, which are not affected as dramatically. Serum E1 values average 30 pg/mL but may be higher in obese women because aromatization increases as a function of the mass of adipose tissue. Estrone sulfate (E1 S) is an estrogen conjugate that serves as a stable-circulating reservoir of estrogen, and its levels are the highest of any estrogen. Serum prolactin levels may be very slightly decreased because prolactin is somewhat influenced by estrogen status. Androstenedione and testosterone levels are lower in women who have experienced bilateral oophorectomy, with values averaging 0. The adrenal gland also continues to produce androstenedione, dehydroepiandrosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate; and, primarily as a function of aging, these values decrease somewhat (adrenopause), although cortisol secretion remains unaffected. Cross-sectional data obtained across the perimenopause have suggested very little early change in secreted androstenedione and testosterone. However, 24-hour mean values have been shown to decline with age and were shown to decrease between the second and fourth decades. The decline in androstenedione after menopause also is greater than that of testosterone; and it is clear that several years after the menopause, levels of androstenedione and testosterone are significantly lower than values in premenopausal women. In the brain, because estrogen receptors are abundant and estrogen is known to influence many brain processes, the absence of estrogen can result in symptomatic as well as physiologic changes. Estrogen is important for blood flow, synaptic activity, neuronal growth, the survival of cholinergic neurons, and many other functions, including cognition. This can occur in the perimenopause when levels characteristically fluctuate widely. Although the proximate cause of the flush remains elusive, the episodes result from a hypothalamic response (probably mediated by catecholamines) as a result of a change in estrogen status. It results in heat dissipation by an increase in peripheral temperature (finger, toe); a decrease in skin resistance, associated with diaphoresis; and a reduction in core body temperature (Fig. In general, estrogen has a positive effect on mood and contributes to a sense of well-being. In an estrogen-deficient state such as occurs after the menopause, a higher incidence of depression (clinical Figure 256-1 Circulating levels of pituitary and steroid hormones in postmenopausal women compared with levels in premenopausal women studied during the first week (days 2 to 4 [D2-4]) of the menstrual cycle. Dementia increases as a function of age and has a higher prevalence in women compared with men.
Buy cheap nemasole 100 mg on-line. Georgia man finds "good" life after HIV diagnosis.